MBR Applications
Membrane bioreactors allows to keep a higher concentration of biomass in the reactor. Thus, higher loads can be treated with a smaller volume.
The cellular retention time of all types of bacteria present in the waste water may be controlled more efficiently, thus processes such nitrification-denitrification and biomass adaptation to specific industrial wastewater are achieved more easily.
Further more, the smaller the pore size of the membranes, the higher range of organic pollutants will be efficiently retained in the system allowing for a higher adaptation of the biomass to treat a wider range of recalcitrant organics such as some pesticides, and pharmaceuticals.
MBR technology is the most suitable wastewater treatment technology for industrial waste water treatment, specially when:
- High organic load
- Seasonal variability
- Low biodegradable organic pollutants
- High quality effluent requirements
- High nitrogen load
- Small footprint requirements

MBR for Water disinfection & reclamation
MBR is a technology suitable for wastewater regeneration as the permeate can be reused in irrigation as it is obtained already disinfected. Pathogens are removed by size exclusion.
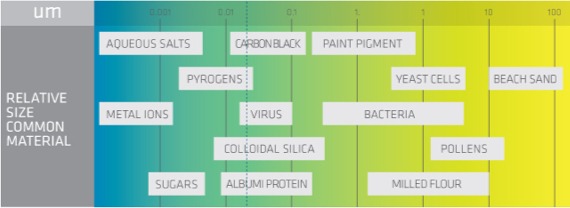
The UF membranes will retain bacteria and most viruses. Commercial UF membranes for MBR applications range in pore size between 0,02 micros and 0,1 microns.
For Example:
- Protozoa range in size from 12 to 60 microns
- Typical cells range in size from 5 to 50 microns.
- Bacteria range in size from about 0.2 to 5 microns.
- Viruses range from 20 nm to 400 nm, e,g
- Pox virus 250-400 nm
- the particle size of hepatitis C virus (HCV) ranges from 30 and 38 nm in diameter
- The particle size of influenza A ranges from 50-120 nm
- Polio virus 25-30 nm
Industrial sectors
- Food industries
- Wineries
- Soft drinks
- Slaughter houses
- Snacks
- Dairies
- Farms
- Fruit processing
- Juice production
- Chemical industries
- Pharmaceuticals and cosmetics
- Plastic recycling companies
Municipal applications
- Where high quality effluent is required (nutrient elimination)
- Small space available
- Expansion of existing plants
- Water reuse