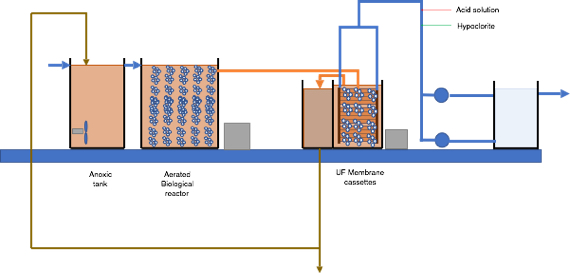
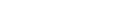MBR design guidelines
The design of a MBR plant involves a good knowledge to consider different and integrate aspects interconnected: to the quality effluent requirements, the characteristics of the company or municipality that generates the wastewater, biological processes, ultrafiltration processes and equipment design.
MBR concepts of interest:
- Permeation flux (flux): The flow rate of filtration per membrane surface area (m3/(m2·d) -> m/d)
- Trans-membrane pressure difference or TMP (Trans Membrane Pressure): The pressure required to obtain filtrate water.
- Specific air demand based on membrane area (SADm) is defined as scouring air flow rate per membrane area.
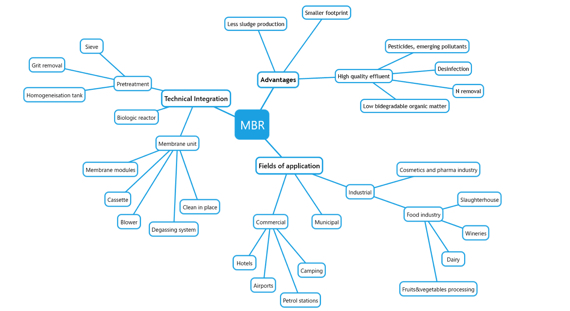
MBR pretreatment
The implementation of a properly designed pretreatment step is critical in MBR plant design to ensure adequate protection of membranes from physical damage, minimize fouling and clogging and the need for cleaning operations.
Preliminary treatment consists of some of the following steps: screening, grit removal, septage handling, odor control, fats and grease removal and flow equalization
- Fine screens should be rotary drum or traveling band screen with either perforated plate or wire mesh. Fine screens should have an opening size between 2 mm – 5 mm for hollow-fiber membranes. In this sense removal of fibrous or stringy material is important and perforated plate is preferred.
- If the influent oil and grease concentration exceeds 100 mg/L, oil and grease removal may also be necessary to prevent membranes from being coated.
- Influent flow equalization shall be considered for all MBR systems: a system with a peak flow rate that is greater than 2.5 times the average daily flow should use equalization storage, or reserve membrane capacity to accommodate the higher peak flow.
- A pH neutralization is frequently necessary in industrial wastewater treatment plants.
MBR bioreactor
- The food to microorganism (F/M) ratio for the reactors should not be greater than 0.1 for plants requiring nitrification and 0.3 for plants not requiring nitrification.
- Bioreactor MLSS concentration should be in the range of 4,000 mg/L to 10,000 mg/L.
- SRT: 10-20 days
- The blowers and piping required for aeration should be installed separately from the blowers and piping required for scouring of the membranes.
- Membrane tank MLSS concentration should be in the range of 4,000 mg/l to 15,000 mg/l.
- Sludge recycle rates for MBR systems range from 200 and 400 percent of influent flow. Sludge recycle pumps must include provisions for operator adjustment
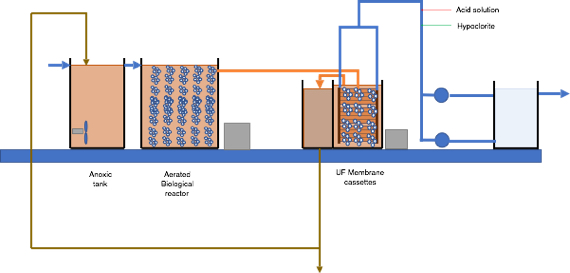
MBR ultrafiltration unit
A complete ultrafiltration unit in MBR application needs several elements that have to be properly designed for an efficient functionality of the membranes. The main elements to consider in the design of an ultrafiltration unit are:
- membrane cassettes: main element of the UF system that will carry out the separation of the solid and the treated water.
- Air scouring system: it has an important role to keep the membranes clean and keep the flux stable. The proper blower has to selected.
- Clean in place system: it plays an important role when chemical cleaning operations are required to recover the functionality of the membranes with use.
- Pumps: ultrafiltration pumps, sludge return pumps, drainage pumps, etc.
- Piping and control valves.
- Tanks: membrane tanks, sludge tank, permeate water tank.
- Control and monitoring equipment: flowmeters, pressure gauges, level control, etc.
- Degassing system
Other elements con consider to help Membrane Maintenance:
- Design the MBR for easy removal of the membrane cassettes for membrane recovery operations considering the membrane cassette wet weight plus additional weight of the solids accumulated on the membranes
- Design the MBR process so that the daily average flow can be treated with one membrane tank out of service. (e.g., 3 design tanks + 1 out of service = 4 total).
- A means of completely emptying each membrane tank of all grit, debris, liquid, and sludge should be provided.
- All equipment should be accessible for inspection, maintenance, and operation.
- A sump should be provided in any basin with a flat bottom.